By: Geraldus Sigap
In recent years, advances in medical technology have revolutionized the way physicians diagnose and treat diseases, particularly in the field of gastroenterology. One of the most remarkable developments is ultrasound endoscopy, also known as endoscopic ultrasound (EUS). This minimally invasive diagnostic tool combines traditional endoscopy with ultrasound imaging to provide detailed visuals of the digestive tract and surrounding organs. For patients experiencing gastrointestinal issues, this technology offers a more comprehensive, accurate, and less invasive alternative for diagnosis.
Ultrasound endoscopy is a cutting-edge procedure that merges two powerful imaging techniques: endoscopy and ultrasound. Traditionally, endoscopy involves using a flexible tube equipped with a camera (endoscope) to visualize the interior of the digestive tract. While this provides a direct view of the mucosal surface, it does not offer insights into the deeper layers or adjacent structures, such as the pancreas, liver, or lymph nodes.
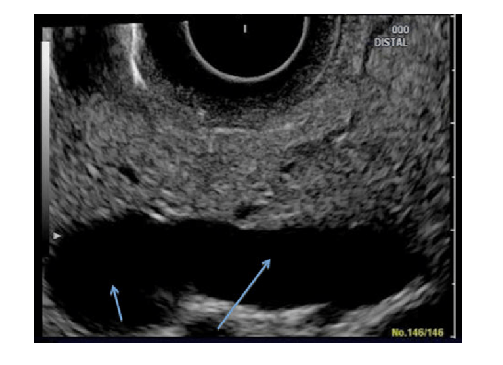
Figure 1. Normal ultrasound endoscopic result
Ultrasound endoscopy, however, enhances this process by attaching an ultrasound probe to the endoscope. This enables physicians to generate high-resolution images of the digestive tract and surrounding tissues, offering a more in-depth assessment. The combination of both modalities provides a unique advantage, as it allows for the evaluation of conditions that might otherwise require more invasive procedures or less effective imaging techniques.
There are several clinical scenarios where ultrasound endoscopy is highly valuable. It is particularly useful for diagnosing and staging cancers of the digestive system, including esophageal, gastric, pancreatic, and rectal cancers. Additionally, EUS is commonly used to evaluate the following conditions:
- Pancreatic Disease: EUS is one of the most accurate tools for diagnosing pancreatic cancer, cysts, and chronic pancreatitis. It provides detailed images of the pancreas and can help detect tumors that are otherwise difficult to identify through other imaging modalities.
- Bile Duct Abnormalities: When investigating gallstones, bile duct blockages, or inflammation, ultrasound endoscopy allows for a thorough examination of the bile ducts. This is crucial for diagnosing conditions like cholangiocarcinoma or bile duct stones.
- Gastrointestinal Cancer Staging: One of the key advantages of EUS is its ability to assess the depth of tumor invasion and the involvement of lymph nodes. Accurate staging is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan for cancers of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Esophageal Diseases: In cases of esophageal cancer, Barrett’s esophagus, or achalasia, EUS provides valuable insights into the extent of the disease. By visualizing the esophageal wall and surrounding structures, physicians can make more informed decisions about the need for surgery or other treatments.
- Submucosal Lesions: EUS is highly effective in evaluating growths or masses located beneath the mucosal surface of the gastrointestinal tract, such as gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). It helps differentiate between benign and malignant growths.
FNA (Fine Needle Aspiration) Guidance: EUS can be paired with fine needle aspiration (FNA) to obtain tissue samples from suspicious areas, including lymph nodes, tumors, or cysts. This provides an opportunity for minimally invasive biopsy, helping to confirm the diagnosis of various conditions.
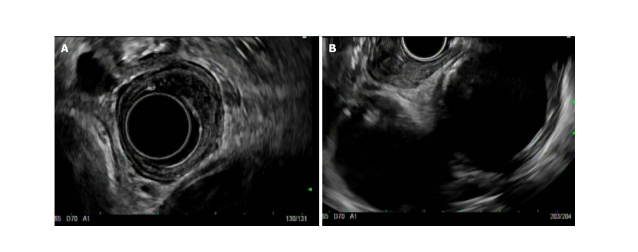
Figure 2. Radial endoscopic ultrasound view of an early esophageal cancer (A) and linear endoscopic ultrasound view of the same lesion (B)
Ultrasound endoscopy is performed by a gastroenterologist or trained specialist. The procedure is typically done on an outpatient basis, meaning that patients can go home the same day. Here’s what to expect:
- Preparation: Patients are advised to avoid eating or drinking for several hours before the procedure to ensure that the stomach is empty. Sedation is usually administered to keep the patient comfortable during the procedure.
- The Procedure: Once the patient is sedated, the endoscope, equipped with the ultrasound probe, is inserted through the mouth or rectum, depending on the area being examined. As the endoscope advances through the digestive tract, the ultrasound transducer emits sound waves that bounce off the surrounding tissues, creating detailed images.
- Image Interpretation: The physician interprets the images generated by the ultrasound in real-time, allowing for immediate diagnosis and evaluation of any abnormalities. If necessary, a fine needle can be passed through the endoscope to perform a biopsy of any suspicious lesions.
- Recovery: After the procedure, patients are monitored for a short time to ensure there are no complications from sedation. Most patients experience little to no discomfort and can resume their normal activities within a day.
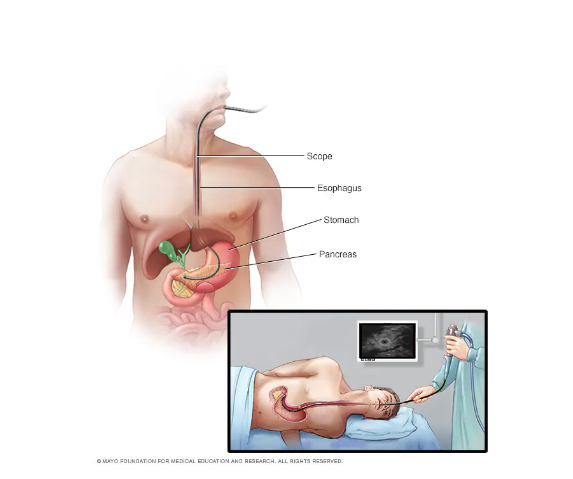
Figure 3. Ultrasound endoscopy
- Minimally invasive: EUS offers a less invasive alternative to exploratory surgery or other diagnostic procedures that may require large incisions.
- High accuracy: With its combination of endoscopy and ultrasound, EUS offers unparalleled precision in diagnosing and staging gastrointestinal cancers, making it a crucial tool in cancer care.
- Faster recovery: Since the procedure is typically done on an outpatient basis with minimal discomfort, patients can return to their normal routines quickly.
- Diagnostic and therapeutic: In addition to its diagnostic capabilities, EUS can also guide therapeutic procedures, such as draining cysts or delivering medication directly to specific areas.
One of the key differentiators of ultrasound endoscopy is its ability to provide both diagnostic imaging and therapeutic intervention in a single procedure. Traditional imaging methods, such as CT scans and MRI, offer useful information about the size and location of tumors or lesions, but they do not provide the same level of detail about the depth of invasion or the involvement of adjacent structures.
For example, while a CT scan can detect a pancreatic tumor, EUS offers more precise information about the tumor’s size, location, and whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes. This detailed information is crucial for determining the stage of cancer and choosing the appropriate treatment plan.
EUS is often recommended when other imaging techniques, such as CT scans or MRIs, are inconclusive, or when more detailed information is required. For patients with unexplained gastrointestinal symptoms, such as abdominal pain, weight loss, or jaundice, EUS can provide the clarity needed for a diagnosis.
Patients with a known diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancer may also undergo EUS to assess the extent of their disease and guide treatment decisions. In these cases, EUS helps ensure that patients receive the most appropriate and effective care.
At Abdi Waluyo Hospital, we are proud to offer state-of-the-art ultrasound endoscopy services to our patients. Our team of experienced gastroenterologists uses the latest technology to provide accurate, minimally invasive diagnoses for a wide range of gastrointestinal conditions. Whether you are dealing with abdominal pain, unexplained symptoms, or a more serious condition like gastrointestinal cancer, our experts are here to provide the care and support you need.
Our advanced endoscopy suite is equipped with the latest ultrasound technology, allowing for precise imaging and diagnosis in real-time. In addition to diagnostic procedures, we offer therapeutic options such as fine needle aspiration and cyst drainage, ensuring that patients receive comprehensive, personalized care.
Resources
- Fig. 2. Normal endoscopic ultrasound image of the pancreas acquired… [Homepage on the Internet]. ResearchGate. [cited 2024 Sep 23];Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Normal-endoscopic-ultrasound-image-of-the-pancreas-acquired-with-a-radial-probe-during_fig12_234702317
- Radlinski M, Shami VM. Role of endoscopic ultrasound in esophageal cancer. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2022;14(4):205–214.
- Endoscopic ultrasound – Mayo Clinic [Homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2024 Sep 23];Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/endoscopic-ultrasound/about/pac-20385171
- Endoscopic ultrasound in oncology: An update of clinical applications in the gastrointestinal tract – PMC [Homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2024 Sep 23];Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5483416/
- Yang J, Zeng Y, Zhang J-W. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided diagnosis and treatment of gastric varices. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2022;14(12):748–758.
