By: Geraldus Sigap
What is Trigeminal Neuralgia?
Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) is a chronic nerve pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve). It causes sudden, sharp, electric shock-like facial pain that usually lasts for a few seconds to minutes.
There are two main types of TN:
- Classic / Idiopathic: Often caused by vascular compression of the trigeminal nerve.
- Secondary: Occurs due to underlying conditions such as stroke, brainstem tumors, multiple sclerosis, and others.
Key Symptoms to Watch For
Common signs of trigeminal neuralgia include:
- Sharp, stabbing, one-sided facial pain, often described as electric shock-like
- Short attacks lasting seconds to minutes
- May occur dozens or even hundreds of times per day
- Triggered by minor stimuli such as touching the face, chewing, shaving, speaking, or even a light breeze
- A dull, persistent ache may follow the initial attack in some cases
Why Does TN Occur? (Causes & Risk Factors)
- Vascular compression of the trigeminal nerve: Small blood vessels pressing on the nerve disrupt its myelin sheath, causing abnormal pain signals.
- Nerve injury or trauma
- Other neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis
- Brainstem or trigeminal nerve lesions or tumors
- Age-related nerve degeneration, making it more common among older adults
How Do Doctors Diagnose TN?
- History & pain assessment: The doctor will ask about the pattern, triggers, location, and frequency of pain.
- Neurological examination: To rule out other nerve lesions or abnormalities.
- MRI / CT scan: To detect vascular compression, tumors, or other structural abnormalities.
- Additional tests (if needed): Nerve electrophysiology, blood tests, etc.
Accurate diagnosis is essential to tailor treatment to the underlying cause.
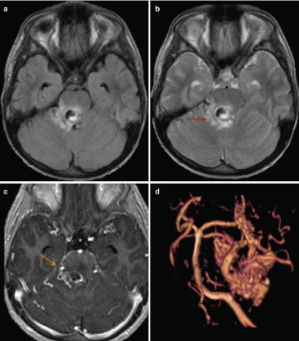
Figure 1. Brain MRI image of a patient with trigeminal neuralgia showing a small blood vessel compression area on the trigeminal nerve.
Treatment & Management Options for TN
Medical Therapy (First-Line Treatment)
- Anticonvulsants / neuropathic pain medications:
- Drugs such as carbamazepine or oxcarbazepine are first-line treatments.
- Tricyclic antidepressants / adjunct medications:
- Used when residual pain persists or when primary drugs cause side effects.
- Local anesthesia / nerve blocks:
- Sometimes used to provide temporary pain relief.
Surgical or Interventional Procedures
If medications fail or cause intolerable side effects, invasive treatments may be considered:
- Microvascular Decompression (MVD):
- A surgical procedure to reposition the blood vessel compressing the trigeminal nerve.
- Gamma Knife / Stereotactic Radiosurgery:
- A non-invasive radiation surgery that targets the pain-causing portion of the nerve.
- Rhizotomy or Trigeminal Nerve Ablation:
- Cutting or damaging selected nerve fibers to stop pain signals.
- Radiofrequency Ablation
- Radiofrequency ablation is one of the latest treatment modalities for trigeminal neuralgia. This procedure uses radio waves to generate controlled heat on the trigeminal nerve fibers that are the source of pain. The main goal is to destroy a small portion of the nerve tissue responsible for pain without damaging the overall nerve function. The advantages of RFA include its minimally invasive nature, relatively quick recovery time, and high success rate in reducing the frequency and intensity of pain.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Consult a neurologist immediately if you experience:
- Recurrent, sharp, electric-like facial pain
- Increasing frequency or intensity of attacks
- Significant side effects from medications
- Accompanying symptoms such as facial numbness, muscle weakness, or speech changes
- No response to conservative treatment
RS Abdi Waluyo has a Brain Center that provides optimal care for neurological conditions, including trigeminal neuralgia. The Neurology and Neurosurgery services at RS Abdi Waluyo offer advanced diagnostic facilities such as MRI 3T / 1.5T, CT scan, brain mapping, EEG, and EMG. If you experience sharp facial pain, don’t ignore it. Consult the Neurology and Neurosurgery specialists at RS Abdi Waluyo today. Call 021-3144989 or book an appointment online via https://abdiwaluyo.com/
Referensi:
- Shankar Kikkeri N, Nagalli S. Trigeminal Neuralgia. [Updated 2024 Mar 3]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan
- Gambeta, E., Chichorro, J. G., & Zamponi, G. W. (2020). Trigeminal neuralgia: An overview from pathophysiology to pharmacological treatments. Molecular pain
- Pasquini, L., Bozzao, A. (2019). Imaging of Trigeminal Neuralgia. In: Cova, M., Stacul, F. (eds) Pain Imaging. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99822-0_6

