By: Geraldus Sigap

Living with chronic conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can be physically and emotionally challenging, often affecting daily routines, work, and social interactions. Many people with these conditions face not only the symptoms but also the stigma of living with an “invisible illness” that others may not fully understand. This makes building awareness and fostering empathy essential for creating a more inclusive and understanding community.
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are both types of inflammatory bowel disease, but they differ in how they affect the digestive system.
Crohn’s Disease: This condition can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus. It often involves deeper layers of the bowel wall and can cause patches of inflammation, leaving unaffected areas in between.
Ulcerative Colitis: Unlike Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis is limited to the colon and rectum. It causes continuous inflammation and ulcers in the innermost lining of the colon.
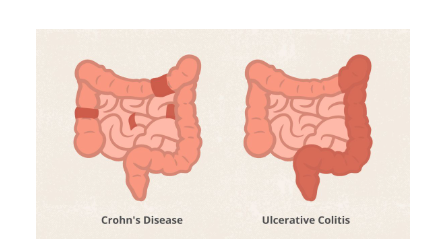
Figure 1. Different location of inflammation on Chron’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
Both conditions can lead to similar symptoms, but the areas they affect and the severity of the inflammation can vary widely from person to person.
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can range from mild to severe and often come in waves, with periods of flare-ups followed by remission. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent diarrhea, often accompanied by an urgent need to use the bathroom
- Abdominal pain and cramping, which can vary in intensity
- Blood in the stool, a result of inflammation and ulcers in the digestive tract
- Fatigue, which may be caused by anemia, inflammation, or poor nutrient absorption
- Weight loss and malnutrition, as inflammation can interfere with digestion and nutrient uptake
These symptoms can be physically exhausting and emotionally draining, affecting not only the individual’s health but also their social, professional, and personal lives.
Living with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis can be a constant struggle, as symptoms may flare up unexpectedly. Many people with these conditions experience a significant impact on their quality of life. The need for frequent bathroom trips, dietary restrictions, and fatigue can make it difficult to maintain a normal routine.
In addition to physical challenges, the stigma surrounding bowel diseases often discourages people from discussing their symptoms openly. This can lead to feelings of isolation and anxiety. Raising awareness about Crohn’s and colitis helps break the silence and promotes a more inclusive and understanding community.
The exact cause of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis is not fully understood, but researchers believe it is a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
- Genetics: Family history plays a role, as people with a relative who has inflammatory bowel disease are at higher risk of developing it.
- Immune System: An abnormal immune response may trigger inflammation in the digestive tract. Instead of protecting the body from infections, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the gut.
- Environmental Factors: Factors such as diet, stress, and exposure to certain bacteria or viruses may influence the development or severity of these conditions.
While these factors contribute to the onset of Crohn’s and colitis, they do not provide a complete picture. Ongoing research aims to uncover more about the mechanisms behind these diseases and develop better treatments.
Crohn’s and Colitis Awareness Week is an opportunity to educate the public about these conditions and highlight the challenges faced by those who live with them. Awareness efforts focus on dispelling myths, encouraging open conversations, and promoting early diagnosis and treatment.
Many people delay seeking medical help for their symptoms, either because they do not realize the seriousness of their condition or because they feel embarrassed. Awareness campaigns aim to change this by normalizing discussions about digestive health and encouraging individuals to prioritize their well-being.
Diagnosing Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis requires a thorough evaluation, as their symptoms overlap with other gastrointestinal conditions. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: The doctor will ask about your symptoms, family history, and lifestyle factors. They may also perform a physical exam to check for signs of inflammation.
- Blood and Stool Tests: These tests can identify inflammation markers, anemia, or infections that may be contributing to symptoms.
- Endoscopic Procedures: A colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy allows the doctor to examine the inside of the digestive tract and take tissue samples for further analysis.
- Imaging Studies: Tests such as CT scans, MRI, or barium X-rays provide detailed images of the digestive tract to identify areas of inflammation or narrowing.
Early diagnosis is crucial for managing symptoms effectively and preventing complications.
While there is no cure for Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, treatments aim to reduce inflammation, manage symptoms, and improve quality of life. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual and may include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors, and biologic therapies can help control inflammation and prevent flare-ups.
- Diet and Nutrition: Dietary adjustments, such as avoiding trigger foods and ensuring adequate nutrient intake, play a key role in managing symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged sections of the digestive tract or address complications.
- Stress Management: Stress can worsen symptoms, so relaxation techniques, counseling, or support groups can be beneficial.
Working closely with a healthcare team ensures that individuals with Crohn’s or colitis receive the most effective care for their specific needs.
At RS Abdi Waluyo, we are proud to announce the establishment of our dedicated Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Center in collaboration with the prestigious University of Chicago. This partnership reflects our commitment to enhancing care for patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, particularly as the prevalence of IBD driven by autoimmune factors continues to rise. Our IBD Center combines advanced diagnostics, personalized treatment plans, and cutting-edge therapies to address the increasing need for more specialized care. With this collaboration, we aim to provide world-class services and innovative solutions, ensuring that every patient receives the best possible support for their journey toward better health and improved quality of life.
Resources
- Crohn’s Disease Versus Ulcerative Colitis: What’s the Difference? [Homepage on the Internet]. EverydayHealth.com. 2024 [cited 2024 Dec 13];Available from: https://www.everydayhealth.com/crohns-disease/symptoms/key-difference-between-crohns-disease-ulcerative-colitis/
- Ranasinghe IR, Tian C, Hsu R. Crohn Disease [Homepage on the Internet]. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2024 [cited 2024 Aug 25]; Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK436021/
- Crohn’s & Colitis UK [Homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2024 Dec 10];Available from: https://crohnsandcolitis.org.uk
- Homepage | Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation [Homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2024 Dec 10];Available from: https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/
