By : Gerladus Sigap
Why Knee Pain Can Affect Your Daily Activities
Knee pain is one of the most common joint complaints, especially among older adults. The condition is often caused by osteoarthritis, a degenerative disease that damages the cartilage, the smooth tissue that cushions the knee joint. When the cartilage wears down, the bones rub against each other, leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty moving.
Other possible causes include old injuries, rheumatoid arthritis, or knee deformities. When the pain becomes severe and conservative treatments such as medication, physiotherapy, or joint injections no longer help, your doctor may recommend a knee replacement surgery as the next step.
What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace the damaged parts of the knee joint with artificial implants (prostheses) made of metal and medical-grade plastic that function like a natural knee. This procedure aims to relieve pain, restore mobility, and improve your ability to walk comfortably again.
There are two main types of knee replacement:
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR): The entire knee joint is replaced.
- Partial Knee Replacement (PKR): Only the damaged part of the joint is replaced, if the rest remains healthy.
When is Knee Replacement Recommended?
Your orthopedic specialist may recommend knee replacement surgery if you experience:
- Severe knee pain that interferes with daily activities such as walking or climbing stairs
- Joint stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Lack of improvement with medication, physiotherapy, or other treatments
- Knee deformities, such as bow-legged (O-shaped) or knock-kneed (X-shaped) alignment
If left untreated, severe knee damage can lead to permanent disability and a significant decline in quality of life.
Preoperative Preparation Before Knee Replacement Surgery
Before undergoing knee replacement surgery, patients will go through several evaluations to ensure that the joint, bone, and surrounding tissues are ready for the procedure.
Key assessments include:
- High-Resolution Knee MRI (3 Tesla MRI), RS Abdi Waluyo is equipped with an advanced 3 Tesla MRI, which provides extremely detailed imaging of the knee joint and soft tissues. This allows doctors to accurately assess the extent of joint damage and plan the surgery with precision.
- Blood and cardiac evaluations to ensure the patient is in good overall condition before surgery.
- Anesthesia consultation to determine the safest and most suitable type of anesthesia.
- Preoperative physiotherapy, designed to strengthen the knee and leg muscles prior to surgery.
With comprehensive preoperative preparation, the surgery can be performed more safely, and the recovery process will yield optimal results.
How is Knee Replacement Surgery Performed?
- General anesthesia is administered to ensure you remain comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
- The surgeon makes a small incision in front of the knee to access the joint.
- The damaged cartilage and bone are carefully removed.
- A custom artificial implant is inserted to replace the damaged joint surfaces.
- Once proper alignment and stability are ensured, the incision is closed and you will be transferred to the recovery room.
- The entire procedure typically takes 1–2 hours, depending on the complexity of the case.
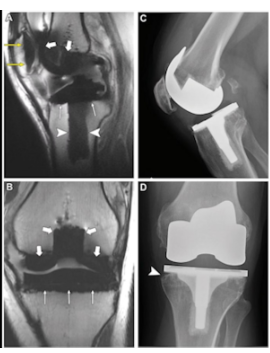
Figure 1. MRI Results of knee replacement surgery
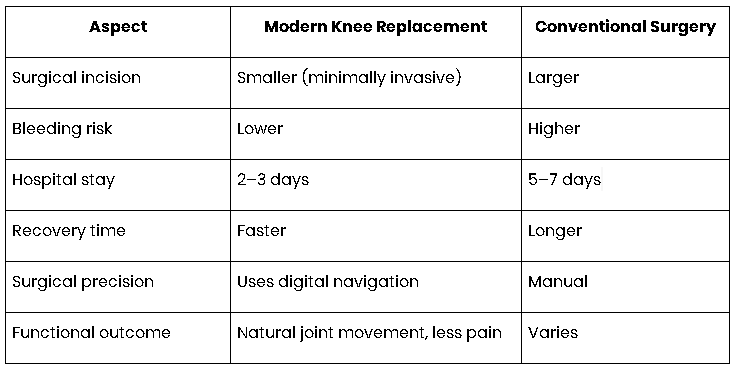
Advantages of Modern Knee Replacement Surgery
Recovery After Knee Replacement Surgery
After surgery, patients are guided by a rehabilitation team to help speed up recovery.
Most patients can stand or walk with assistance within 24 hours after the operation.
Typical recovery timeline:
- Days 1–3: Begin sitting and standing with physiotherapist assistance
- Weeks 1–2: Start walking with a walker or cane
- Weeks 4–6: Improved muscle strength and reduced pain
- After 3 months: Gradual return to normal daily activities
A structured rehabilitation and physiotherapy program plays a vital role in restoring knee strength and flexibility after surgery.
RS Abdi Waluyo has a dedicated Orthopedic Clinic with state-of-the-art facilities and experienced orthopedic surgeons specializing in modern knee replacement procedures. If you or a loved one suffer from chronic knee pain, stiffness, or difficulty walking, don’t wait until it gets worse. Rehabilitation after surgery is the most crucial stage in achieving the best possible outcome. At RS Abdi Waluyo, patients receive personalized care at the Physiotherapy Center, equipped with modern facilities and guided by experienced physiotherapists. Each rehabilitation program is tailored to help patients regain muscle strength, joint flexibility, and walking ability step by step, ensuring a smooth and complete recovery.
Consult the Orthopedic Specialist Team at RS Abdi Waluyo, who are experienced in modern, minimally invasive knee replacement techniques. Call 021-3144989 or make an appointment online via https://abdiwaluyo.com/ today.
FAQ
- Is knee replacement surgery safe?
Yes. It is a highly successful and safe procedure, especially when performed by skilled orthopedic surgeons in a modern hospital like RS Abdi Waluyo.
- How long does it take to recover after surgery?
Most patients can walk with assistance within 1–2 days after surgery and return to light activities within 4–6 weeks, depending on individual health and recovery progress.
- How long do knee implants last?
Modern implants are designed to last 15–20 years or longer, depending on your activity level and lifestyle.
- Can elderly patients undergo this surgery?
Yes. Knee replacement surgery is safe for elderly patients as long as their overall health, such as heart, lung, and blood pressure, is stable. Preoperative evaluations are conducted to ensure safety.
- When should I consider knee replacement surgery?
If knee pain interferes with daily life, walking, or sleep and no longer improves with medication or physiotherapy, it’s time to consult an orthopedic specialist to evaluate your suitability for surgery.
References:
- Price, A. J., Alvand, A., Troelsen, A., Katz, J. N., Hooper, G., Gray, A., Carr, A., & Beard, D. (2018). Knee replacement. Lancet (London, England), 392(10158), 1672–1682.
- Gemayel AC, Varacallo MA. Total Knee Replacement Techniques. [Updated 2023 Aug 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538208/
- Endo Y, Burge AJ, Koff MF, Lin B, Westrich GH, Boettner F, Chiu YF, Potter HG. Diagnostic performance of MRI for component loosening in total knee arthroplasty compared with radiography. Radiology. 2022;304(1):128–136

