By: Geraldus Sigap
Kidney stones are a common and often painful condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The formation of these hard mineral deposits in the kidneys can lead to severe discomfort, urinary tract infections, and even kidney damage if not properly diagnosed and treated. For decades, the medical community has relied on imaging techniques such as X-rays, ultrasound, and traditional CT scans to detect and evaluate kidney stones. However, advancements in technology have led to the development of more precise and accurate diagnostic tools, with the CT Naeotom Alpha standing at the forefront of this revolution.
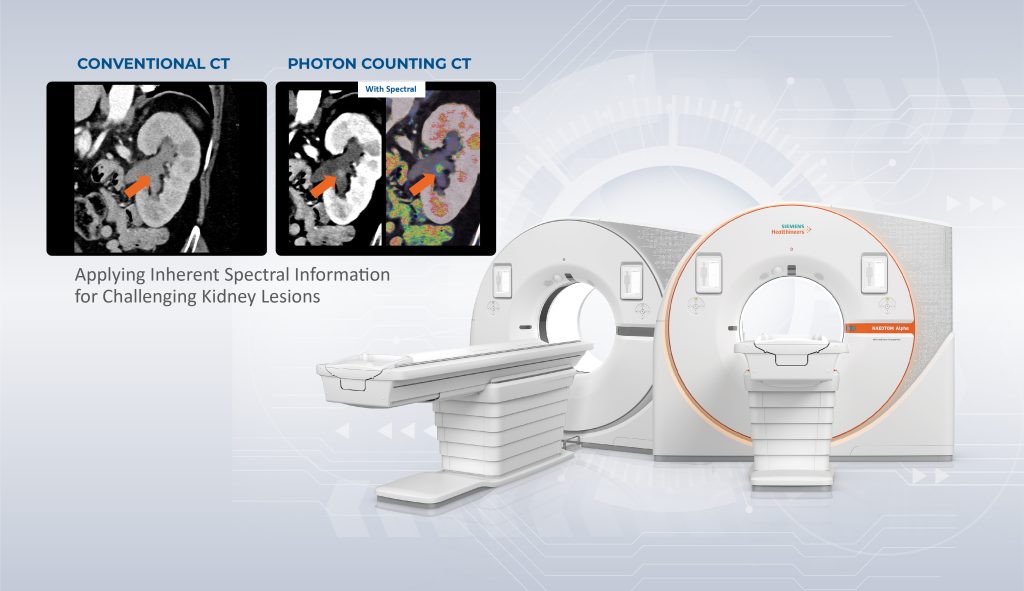
Figure 1. The CT Naetom Alpha
Enter the CT Naeotom Alpha, the world’s first photon-counting CT scanner. Developed by Siemens Healthineers, this cutting-edge technology represents a significant leap forward in medical imaging. Unlike conventional CT scanners that measure the total energy deposited by X-rays passing through the body, photon-counting CT directly detects individual X-ray photons, allowing for much higher resolution images with significantly reduced noise. This capability is particularly beneficial for detecting kidney stones, as it enables the visualization of even the smallest stones with exceptional clarity. The precision offered by the CT Naeotom Alpha is unparalleled. By providing high-resolution images with minimal radiation exposure, this scanner allows for the detection of kidney stones that might otherwise go unnoticed with traditional imaging techniques. This is crucial for early intervention and treatment, as smaller stones are often easier to manage and less likely to cause complications than larger, more established stones.
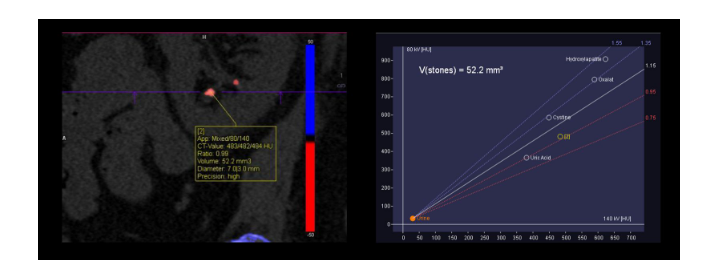
Figure 2. Kidney stones found through CT Naetom Alpha
Moreover, the ability of the CT Naeotom Alpha to differentiate between different types of tissues and materials means that it can provide detailed information about the composition of kidney stones. Understanding the composition of a stone is vital for determining the most appropriate treatment approach, whether it be medication, lithotripsy, or surgical removal. For example, stones composed of calcium oxalate may require different management strategies than those made of uric acid or struvite. The comparison of traditional X-ray, conventional CT scan, and the CT Naeotom Alpha is described through the table below:
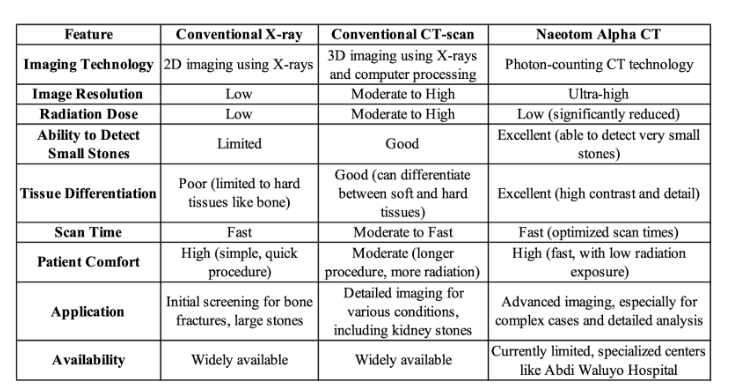
Table 1. Comparison of conventional X-ray, conventional CT-scan, and Naetom Alpha CT
The introduction of the CT Naeotom Alpha at RS Abdi Waluyo is a game-changer for patient care. This advanced technology not only improves the accuracy of kidney stone detection but also enhances the overall patient experience. With faster scan times and lower radiation doses, patients can undergo diagnostic imaging with greater comfort and peace of mind. Additionally, the high level of detail provided by the CT Naeotom Alpha allows healthcare providers to develop more targeted and effective treatment plans, ultimately leading to better outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
For individuals who suffer from recurrent kidney stones or those at high risk of developing them, regular monitoring with the CT Naeotom Alpha can be an invaluable tool in preventing future episodes. By catching stones early and accurately assessing their size and composition, medical professionals can take proactive steps to prevent complications and improve the patient’s quality of life.
At Abdi Waluyo Hospital, we are proud to offer the revolutionary CT Naeotom Alpha scanner as part of our comprehensive diagnostic services. Our commitment to providing the highest standard of care means that our patients have access to the latest and most advanced medical technologies available. Whether you are experiencing symptoms of kidney stones or require regular monitoring, our state-of-the-art imaging facilities ensure that you receive the most accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Resources
- Ebrahimi S, Mariano V. Image Quality Improvement in Kidney Stone Detection on Computed Tomography Images. J Image Graph 2015;3.
- Kidney stone analysis techniques and the role of major and trace elements on their pathogenesis: a review – PMC [Homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2024 Aug 14];Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5418413/
- A deep learning system for automated kidney stone detection and volumetric segmentation on non-contrast CT scans – PMC [Homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2024 Aug 14];Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10407943/
