By: Thalia Kaylyn Averil
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) uses fluoroscopy techniques to digitally remove objects such as bone from the image to better visualize blood vessels. This technique is mainly used for brain blood vessels so it is often referred to as cerebral angiography. Doctors will insert a catheter into a blood vessel during the procedure to inject contrast that will make the blood vessel visible on X-ray. This procedure is mainly performed if the results of other examinations are insufficient. Angiography is still the gold standard and is considered the most sensitive and accurate technique for diagnosing several diseases, although CT scans and MRI scans can already detect various brain-related problems. This procedure is often performed after a CT scan and MRI to obtain more detailed information if abnormal results are found. Before performing DSA, it is important to understand the patient’s condition and any possible risks by consulting a neurologist.
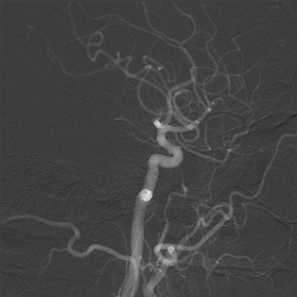
Figure 1. Results of Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA).
Cerebral angiography can visualize blood vessels inside and around the brain specifically. This can aid in the diagnosis of diseases.
- Aneurysm (swollen blood vessels)
- Stenosis (narrowing of blood vessels)
- Atherosclerosis (accumulation of plaque that causes narrowing of blood vessels)
- Vasculitis (inflammation that causes narrowing of the blood vessels)
- Arteriovenous malformations (abnormal connections between arteries and veins)
- Thrombosis (blood clot)
- Vasospasm (abnormal narrowing of blood vessels)
- Total occlusion of blood vessels
Apart from that, angiography also plays a role in interventional radiology.
- Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR)
- Balloon angioplasty to dilate blood vessels
- Stents to keep blood vessels open
- Endovascular embolization to block aberrant blood vessels
- Thrombectomy to remove blood clots
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) procedures vary depending on the patient’s condition and the available healthcare facilities. In general, the following are the procedures performed during Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA).
- The patient is asked to remove clothing, jewelry, hair clips, dentures, or other objects that may interfere during the procedure.
- The patient is asked to empty the bladder before the procedure begins.
- The patient is positioned on the X-ray table.
- The patient is connected to an electrocardiogram (ECG) monitor that records the heart’s electrical activity. In addition, vital signs (such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate) and neurological signs are also monitored during the procedure.
- Before starting the procedure, the patient is given a mild sedative to help the patient relax.
- A catheter will be inserted into an artery in the neck, arm, or groin after the skin has been cleaned.
- If the catheter is inserted into an artery in the arm or groin, the pulse at that location will be checked and marked. Apart from that, the hair in that area will also be shaved. After that, the catheter will be guided into the neck using a special type of X-ray known as fluoroscopy to confirm the location of the catheter in the patient’s body.
- If a catheter is inserted into an artery in the neck, a pillow will be placed under the shoulder to keep the neck extended. The patient’s head will be held in place with a strap or adhesive to prevent the risk of damage to the arteries when moving the head.
- A contrast dye injection is administered, which makes blood vessels visible in X-ray images, allowing doctors to see the blood vessel structures more clearly. Patients will likely experience some generally short-lived effects when contrast dye is injected into the catheter, such as a warm sensation, a salty or metallic taste in the mouth, headache, nausea, or vomiting.
- The patient should notify the radiologist if they experience difficulty breathing, sweating, numbness, or heart palpitations.
- Contrast dye may be injected one or more times.
- After the contrast dye is injected, a series of X-ray images are taken.
- Once the procedure is complete, the catheter is removed and pressure is applied at the site where the catheter was inserted to prevent bleeding.
- Once the bleeding stops, the location is bandaged. A fairly heavy object may be placed over the location to prevent further bleeding or hematoma formation.
DSA is a very effective diagnostic technique for finding out the cause of persistent symptoms related to cerebrovascular disease, such as headaches, because of its ability to provide detailed images and evaluate cerebral blood vessels. Despite some limitations, this method is still the gold standard for assessing cerebrovascular disease. This method is very useful for identifying problems with blood vessels and evaluating alternative pathways of blood flow which is very important for understanding the movement of blood through the vessels in the brain. The diagnosis of other cerebrovascular diseases can also be made by imaging methods such as CT and MR angiography, but DSA is still the gold standard.
Resources
- Mount Sinai Health System. Cerebral angiography [Internet]. New York: Mount Sinai Health System; date of publication unknown [cited 2024 Jun 23]. Available from: https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/tests/cerebral-angiography
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. Cerebral arteriogram [Internet]. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Medicine; date of publication unknown [cited 2024 Jun 23]. Available from: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/cerebral-arteriogram
- Radiopaedia. Digital subtraction angiography [Internet]. Victoria: Radiopaedia; date of publication unknown [revised 2022 Jan 11] [cited 2024 Jun 23]. Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/digital-subtraction-angiography
- Specialist Endovascular Services. Cerebral angiogram [Internet]. New South Wales: Specialist Endovascular Services; date of publication unknown [cited 2024 Jun 23]. Available from: https://sevs.com.au/inr/cerebral-angiogram
