By: Geraldus Sigap
Prostate health is a crucial aspect of men’s overall well-being, yet it often remains shrouded in silence until serious symptoms arise. Traditional diagnostic methods, such as digital rectal exams (DRE) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests, have long been the standard in detecting prostate issues, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer. However, these methods have significant limitations, leading to missed diagnoses or unnecessary procedures. The advent of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has revolutionized the way prostate health is assessed, offering unparalleled precision and reliability that outshines traditional diagnostics.
For years, the combination of DRE and PSA tests has been the frontline approach in screening for prostate abnormalities. While these methods have their merits, they are far from foolproof. The DRE, which involves a physical examination of the prostate via the rectum, is subjective and highly dependent on the examiner’s experience. It can miss small or deep-seated tumors and often cannot differentiate between benign and malignant growths. PSA testing, on the other hand, measures the level of prostate-specific antigen in the blood, which can be elevated in conditions other than cancer, such as prostatitis or BPH. This lack of specificity can lead to unnecessary biopsies and anxiety for patients. Moreover, PSA levels do not always correlate with the presence or severity of prostate cancer. Some men with prostate cancer may have normal PSA levels, while others with elevated PSA may not have cancer at all. This diagnostic ambiguity can result in either over-treatment or under-treatment, neither of which is ideal for patient outcomes.
If there are strong suspicions of cancer, the next step might be a biopsy, where small samples of prostate tissue are taken for examination. However, biopsies can sometimes miss cancerous areas, especially if the sampling is not precise. This is where MRI steps in as a superior tool.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) offers a more accurate and less invasive alternative for diagnosing prostate conditions. Unlike traditional methods, MRI provides high-resolution images that allow for detailed visualization of the prostate gland, surrounding tissues, and any abnormalities that may be present. The ability of MRI to differentiate between various types of tissues makes it particularly effective in identifying tumors, determining their exact location, and assessing their aggressiveness.
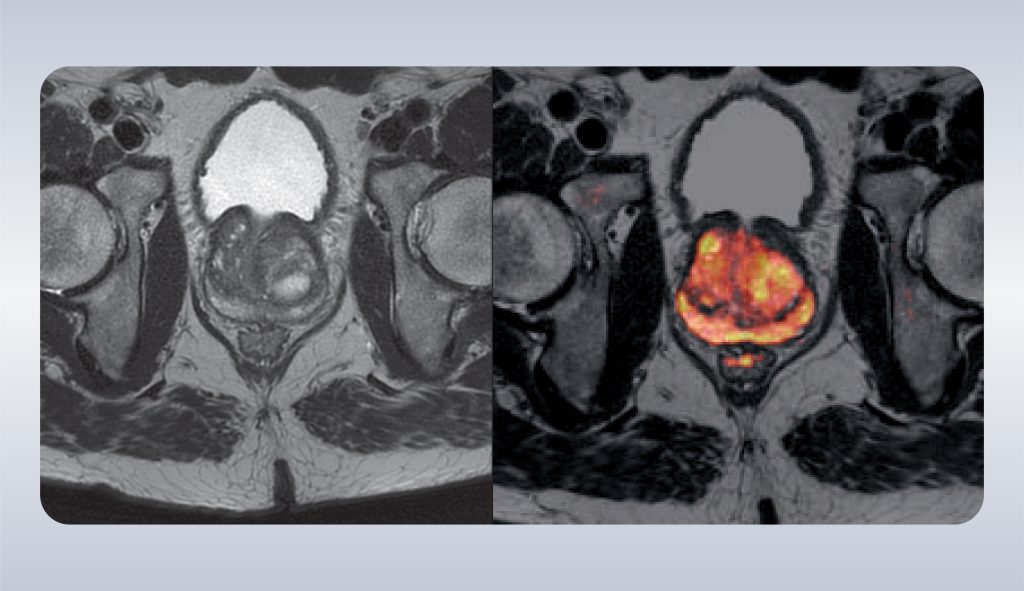
Figure 1. MRI findings on prostate cancer
MRI is especially beneficial in guiding biopsies. Traditionally, prostate biopsies are performed blindly or with the assistance of ultrasound, which does not provide the same level of detail as MRI. This can result in missed tumors or inadequate sampling of suspicious areas. MRI-guided biopsies, however, allow for precise targeting of abnormal regions within the prostate, improving the accuracy of the biopsy and reducing the need for repeat procedures.
Furthermore, MRI can be used to monitor prostate health over time, providing a non-invasive way to track the progression of conditions like BPH or low-risk prostate cancer. This is particularly valuable in active surveillance protocols, where the goal is to monitor the disease without immediate treatment. MRI’s ability to provide clear, detailed images helps ensure that any changes in the prostate are detected early, allowing for timely intervention if necessary. When discussing MRI results, you may hear about the PI-RADS classification system, which stands for Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System. PI-RADS is a standardized system used by radiologists to assess and report the likelihood of prostate cancer based on MRI findings.
PI-RADS scores range from 1 to 5:
- PI-RADS 1: Very low likelihood of clinically significant cancer.
- PI-RADS 2: Low likelihood of clinically significant cancer.
- PI-RADS 3: Intermediate, equivocal (uncertain) likelihood of clinically significant cancer.
- PI-RADS 4: High likelihood of clinically significant cancer.
- PI-RADS 5: Very high likelihood of clinically significant cancer.
At Abdi Waluyo Hospital, we are dedicated to providing the highest standard of care for prostate health. Our facility is equipped with state-of-the-art MRI technology, which plays a critical role in early detection and precise diagnosis of prostate conditions. What sets us apart is our team of highly specialized radiologists, including those with a subspecialty in prostate mapping.
Prostate mapping is a sophisticated technique that involves detailed imaging to determine the exact location of suspicious lesions within the prostate. This level of precision is essential for planning targeted biopsies and treatments, ensuring that no area of concern is overlooked. Our state-of-the-art MRI technology provides a comprehensive and detailed assessment of prostate health, far surpassing the capabilities of traditional diagnostic methods. Whether you are experiencing symptoms or are at risk of prostate issues due to age or family history, our MRI diagnostic services can provide the clarity and confidence you need to make informed decisions about your health.
Resources
- The utility of magnetic resonance imaging in prostate cancer diagnosis in the Australian setting – PMC [Homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2024 Aug 15];Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8988779/
- Sugeha M, Juliantara IPE, Dharmawan I. PROSEDUR PEMERIKSAAN MRI (MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING) PROSTAT PADA KASUS BENIGN PROSTAT HYPERPLASIA. J Ilmu Kedokt Dan Kesehat 2024;11:565–572
- Magnetic resonance imaging in prostate cancer | Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases [Homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2024 Aug 15];Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/4500767
