Oleh: Thalia Kaylyn Averil
Pacemaker atau alat pacu jantung adalah perangkat kecil yang menghasilkan sinyal listrik untuk mengontrol irama jantung sehingga jantung berdetak teratur dan mencegah terjadinya aritmia. Aritmia dapat menyebabkan jantung berdetak terlalu cepat, terlalu lambat, atau tidak teratur. Pasien yang membutuhkan alat pacu jantung seringkali mengalami gejala-gejala seperti pusing, lemas, lelah, pingsan, atau kesulitan berolahraga. Gejala tersebut sering terjadi karena irama jantung yang terlalu lambat, masalah di nodus sinoatrial di jantung, atau masalah dengan konduksi listrik antara bagian-bagian jantung. Alat pacu jantung juga dapat digunakan untuk pasien dengan gejala penyumbatan jantung dan gagal jantung. Alat ini bekerja dengan mengirimkan sinyal listrik untuk membantu jantung mempertahankan ritme yang teratur dan tepat. Selain itu, alat ini juga dapat mengatur detak jantung untuk meningkatkan efisiensi sirkulasi darah ke seluruh tubuh.
Apa itu nodus sinoatrial? Bagaimana pengaturan irama jantung yang normal?
Detak jantung diinisiasi oleh jantung itu sendiri. Beberapa sel otot jantung dapat berkontraksi dan berelaksasi dengan sendirinya tanpa memerlukan sinyal dari sistem saraf. Namun, masing-masing sel otot jantung memiliki ritme alaminya sendiri untuk berkontraksi, tetapi sel-sel tersebut dapat berkontraksi secara bersamaan karena diatur oleh sekelompok sel khusus yang terletak di dinding jantung bagian kanan. Sel-sel tersebut disebut sebagai nodus sinoatrial (SA) yang bertindak seperti alat pacu jantung alami dengan mengatur kecepatan dan waktu bagi semua sel otot jantung untuk berkontraksi bersama. Nodus SA menghasilkan sinyal listrik yang mirip dengan sel saraf dan dapat menyebar dengan cepat karena sel-sel otot jantung saling terhubung melalui sebuah jaringan.
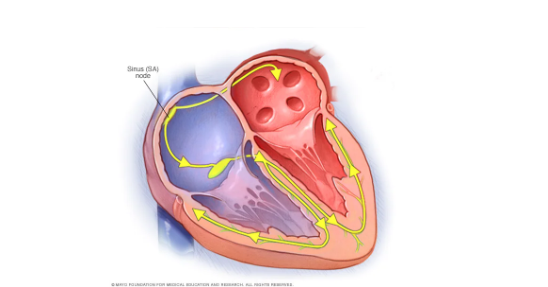
Gambar 1. Nodus sinoatrial.
Alat pacu jantung terdiri dari generator untuk pulsa (denyut nadi) dan lead atau elektroda. Generator pulsa adalah kotak logam kecil yang berisi baterai dan komponen listrik lainnya yang berfungsi untuk menghasilkan arus listrik yang menstimulasi otot jantung. Generator pulsa biasanya ditempatkan di bawah kulit di bagian bawah dada, lebih tepatnya di bawah tulang selangka. Lead atau elektroda adalah kabel fleksibel yang terdiri atas satu sampai tiga kabel untuk dimasukkan ke dalam ruang jantung. Kabel ini dapat mengirimkan sinyal listrik yang diperlukan untuk memperbaiki detak jantung dari generator pulsa.
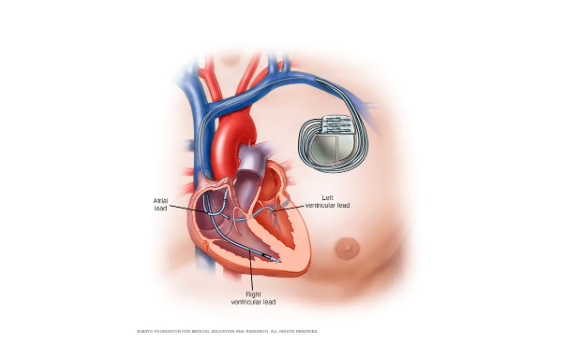
Gambar 2. Alat pacu jantung.
Pemilihan jenis alat pacu jantung bergantung pada gejala dan kondisi jantung pasien. Pasien akan dievaluasi oleh tenaga kesehatan terlebih dahulu sebelum menentukan jenis alat pacu jantung yang digunakan. Ada tiga jenis utama alat pacu jantung:
- Single chamber/bilik tunggal
Alat pacu jantung jenis ini memiliki satu kabel untuk pengiriman sinyal listrik yang menghubungkan ke ruang jantung atas atau bawah, umumnya ke ruang jantung bawah bagian kanan. Namun, alat pacu jantung bilik tunggal juga dapat dihubungkan ke ruang jantung atas bagian kanan. Letak alat pacu jantung ini dipengaruhi oleh kebutuhan dan gejala yang dialami oleh pasien.
- Dual chamber/bilik ganda
Alat pacu jantung bilik ganda memiliki dua kabel untuk pengiriman sinyal listrik yang menghubungkan ke ruang jantung atas dan ruang jantung bawah, umumnya ke jantung kanan. Sama seperti alat pacu jantung bilik tunggal, letak alat pacu jantung dipengaruhi oleh kebutuhan dan gejala yang dialami oleh pasien.
- Biventricular/biventrikular
Alat pacu jantung biventrikular juga dikenal sebagai alat untuk cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) atau terapi sinkronisasi ulang jantung. Pada umumnya, alat pacu jantung jenis ini digunakan untuk pasien dengan gagal jantung dan detak jantung yang lebih lambat dari normalnya. Gagal jantung seringkali disebabkan karena kedua ruang jantung bawah tidak dapat memompa secara bersamaan. Dengan menggunakan tiga kabel yang terhubung ke ruang jantung atas bagian kanan dan ruang jantung bawah bagian kanan serta kiri, alat ini dapat memperkuat kinerja otot jantung dan mengatur kontraksi pada ruang jantung bawah agar berkontraksi secara bersamaan. Koordinasi ini membantu jantung untuk memompa darah lebih efisien dan dapat meringankan gejala gagal jantung.
Sebelum prosedur pemasangan alat pacu jantung, Anda akan diminta untuk tidak makan atau minum apapun selama delapan jam, beberapa obat juga perlu berhenti dikonsumsi. Untuk implantasi alat pacu jantung ke dalam tubuh, intervensi bedah yang umumnya memerlukan waktu beberapa jam untuk menyelesaikannya diperlukan. Setelah prosedur selesai, Anda dapat dipulangkan pada hari yang sama atau monitor selama beberapa jam, sesuai dengan kondisi kesehatan Anda. Banyak pasien dapat melanjutkan aktivitas normalnya dalam beberapa hari, tetapi mengangkat beban berat atau gerakan lengan yang berat harus dihindari selama beberapa minggu. Umumnya, pola makan Anda juga dapat kembali seperti semula jika tidak terjadi komplikasi. Anda dianjurkan untuk melakukan pemeriksaan kesehatan rutin setelah pemasangan alat pacu jantung, konsultasikan hal ini bersama dengan tenaga kesehatan Anda untuk menentukan frekuensi pemeriksaan ini.
Referensi:
- Urry LA, Cain ML, Minorsky PV, Wasseman SA, Reece JB. Campbell Biology. 12th ed. New York: Pearson Education; 2021.
- Mayo Clinic. Pacemaker [Internet]. Rochester: Mayo Clinic; date of publication unknown [cited 2024 Apr 9]. Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/pacemaker/about/pac-20384689
- Stanford Medicine. Types of pacemakers [Internet]. Stanford: Stanford Medicine; date of publication unknown [cited 2024 Apr 9]. Available from: https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-treatments/p/pacemaker/types.html
